Flood Control Infrastructure and Historic Floods
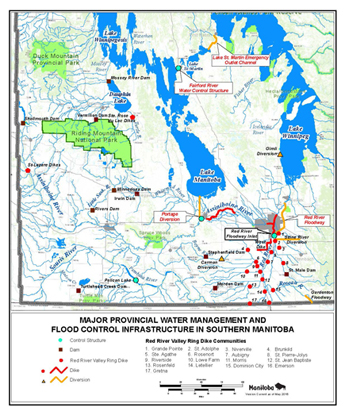 Southern Manitoba has extensive flood control measures in place, particularly in the Red River Valley, from Winnipeg, south to the U.S. border. Flood controls were built after the devastating flood of 1950, which flooded the Red River Valley and the City of Winnipeg. Construction of the Red River Floodway, the Portage Diversion and the Shellmouth Dam and Reservoir began in the mid 1960's. Additional flood control improvements, including an expansion of the Red River Floodway, were made after the 1997 flood. This flood was substantially larger than the 1950 flood, but resulted in far less property damage because of the flood control measures in place. There are also flood control measures along the Assiniboine River.
Southern Manitoba has extensive flood control measures in place, particularly in the Red River Valley, from Winnipeg, south to the U.S. border. Flood controls were built after the devastating flood of 1950, which flooded the Red River Valley and the City of Winnipeg. Construction of the Red River Floodway, the Portage Diversion and the Shellmouth Dam and Reservoir began in the mid 1960's. Additional flood control improvements, including an expansion of the Red River Floodway, were made after the 1997 flood. This flood was substantially larger than the 1950 flood, but resulted in far less property damage because of the flood control measures in place. There are also flood control measures along the Assiniboine River.
The largest flood in the recorded history of Manitoba took place on the Red River in 1826 and was 40 percent larger than the 1997 flood. It is estimated that a repeat of an 1826 level flood without the Red River Floodway would result in more than $5 billion in damages for the province.
Investments into the flood protection are estimated to have prevented tens of billions of dollars in damages throughout Manitoba over the years. The system mitigates human risk and infrastructure damage during flood events resulting in a considerable decrease in the number of properties damaged and the number of people evacuated during spring floods.
The 2011 flood affected a large geographic area and thousands of Manitobans. Early flood forecasts and flood-mitigation efforts helped many communities get a head start on protecting homes and lands, but damage was still widespread.
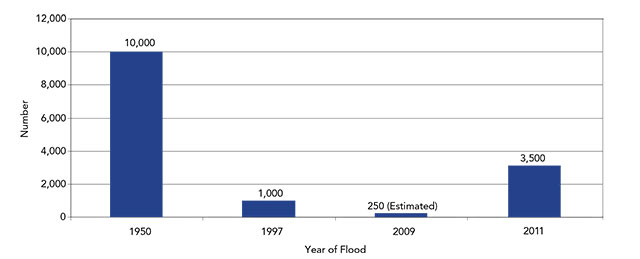
Number of homes damaged
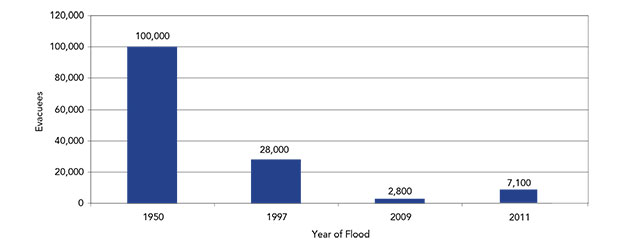
Number of people evacuated
Red River Basin
The Red River runs north through the Red River Valley, forming the border of Minnesota and North Dakota. The river enters Manitoba near Emerson, passes through Winnipeg and empties into Lake Winnipeg. The river is approximately 885 km (550 miles).The last major floods along the Red River were in 1950, 1979, 1997, 2009, 2011 and 2017.
 Red River Floodway |
 Community and Individual Flood Protection |
|
 Other Flood Protection |
 Historic Floods |
Assiniboine River Basin
The Assiniboine River runs from southern Saskatchewan and ends when it meets the Red River in the City of Winnipeg. The river twists and turns for approximately 1,070 km (665 miles). The last major floods along the Assiniboine River were in 1976, 1995, 2011, 2014 and 2017.
 Shellmouth Dam and Reservoir |
 Portage Diversion |
 Assiniboine River Dikes |
 Community and Individual Flood Protection |
 Other Flood Protection |
 Historic Floods |
Major Lakes and their Basins
Water levels on Manitoba’s large lakes are subject to the weather conditions in their larger basins. Lake Manitoba and Lake St. Martin have a long history of both high and low lake levels depending on the inflows, once largely determined by climate and weather conditions. A number of water control structures have been constructed to better control water levels on these lakes.
 Lake Manitoba |
 Lake St. Martin Emergency Outlet Channel |
 Fairford River Water Control Structure |
 Lake Winnipeg |
 Community and Individual Flood Protection |
 Historic Floods |


